Automation offers multiple benefits over traditional manual systems – faster, more repeatable measurements increase engine build to nearly 100% right the first time.
For years, turbine engine builders have relied on manual processes for measurement and stacking to turbine alignment. These processes can be slow and rely on the skill of the operator. Automating this process is key to increasing throughput and improving engine yield while maintaining accuracy.
Aero-engine cores are constructed of multiple separate components, known as a rotor, blisk, disk, or stage. For the engine to run efficiently, smoothly, and safely this rotating assembly must be accurately aligned. A typical High-Pressure Compressor (HPCR) or High-Pressure Turbine (HPTR) would consist of 6 components, with each component joined to make the complete assembly. Individual components mate together through an interference fit of snap surfaces making parameters such as squareness and eccentricity critical to performance.
Axis movement, component alignment, gauge contact, feature measurement, and result reporting are all completed seamlessly with predefined routines, “Operator intervention is all but eliminated with robotic style automation”.
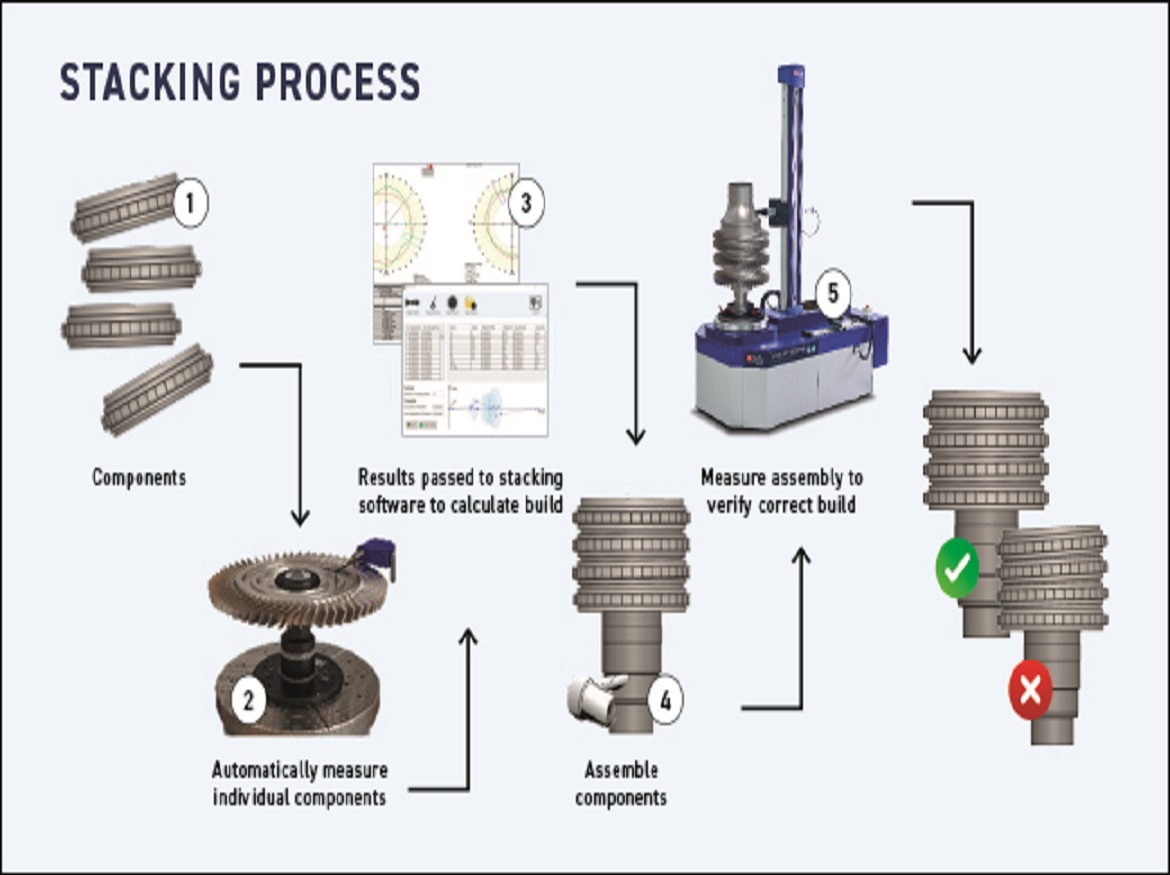
Automation of turbine measurement and stacking offers further improvements including, repeatability, and consistency between sites and operators, vastly improving build quality. This delivers fully optimized module straightness while minimizing runout. By utilizing axial and radial rotor measurements on individual components, best assembly build configurations can be calculated to meet optimal performance for High-Pressure Compressors (HPCR) and High-Pressure Turbines (HPTR). The full Taylor Hobson stacking process is illustrated below.
- Identify components
- Automatically measure each individual component
- Measurement results are passed to stacking software to calculate the build
- Assemble components
- Measure assembly to verify the correct turbine build
As major turbine manufacturers struggle with demand, it is important that speed and throughput are increased without losing accuracy and consistency.
With this in mind, Taylor Hobson has developed the line of AEROStack Systems to address the needs of the turbine market with automated turbine rotor measurement, alignment, and assembly. Delivering the complete solution; from the measurement system through to part holding and stack optimization, using TALYStack software. All of these critical aspects can be tailored to suit any engine program whether its OEM or aftermarket, measuring individual rotors and complete assemblies.
Further improving the measurement process, AEROStack Systems offers diameter measurement capability, enabling measurement of blade tips and other sealing surfaces. Measure tip clearance and diameter in less than half the time when compared to other techniques.
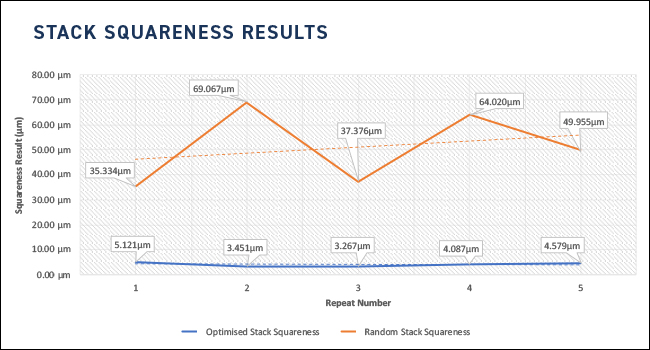
PREDICTED STACK AGAINST RANDOM STACKING
Unique gauging, repeatability, and reproducibility, combined with the dedicated TALYStack software enable nearly 100% first-time build of engines with the added advantage of a tighter specification.
The example below highlights how stacking parts in an arbitrary manner 5 times, generates high Squareness errors up to 69 µm. Rebuilding the stack in the optimized squareness positions 5 times achieves a much lower overall squareness value with a spread of less than 2 µm, as shown in the graph.
Taylor Hobson provides the ability to use your own build algorithms or take advantage of our TALYStack software.
AXIAL STRAIGHTNESS ANALYSIS
One of the most important parameters for stacking is the Axial Straightness parameter, which calculates the straightness of the rotary axis, giving an indication of the alignment of the rotary axis. This has a large impact on engine efficiency by enabling a reduced rotor to stator clearance but also reduces the time between maintenance by reducing vibration and increasing engine life. TALYStack software provides key aero engine and turbine build specific parameters including…
- Squareness & Squareness Angle
- Radial & Axial Runout (Eccentricity)
- Stack Build Angles
AEROStack Systems also delivers additional metrology parameters including…
- Roundness
- Roughness
- Cylindricity
- Straightness
- Parallelism
- Flatness
- Concentricity
- Coaxiality
Thanks to the introduction of our automated AEROStack Systems, Taylor Hobson now has products standardized globally for several leading jet engine programs, including OEMs and MROs.
Our global support network enables the replication of any engine build program throughout the world, with peace of mind. In recent installations, cycle times have been more than halved. Automation also reduces operator intervention, human error, training time, and variability.
One commercial airline commented, “It takes weeks to train a technician on the manual system, but with the AEROStack System they can train new technicians in hours”.
POWERFUL OPTIMIZATION SOFTWARE
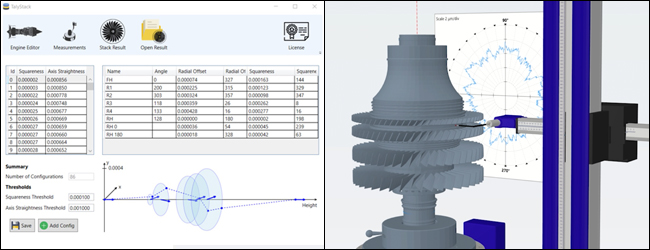
TALYStack & Metrology 4.0
A key feature of Metrology 4.0 Software is a live virtual display that utilizes CAD models for easy visualization and programming.
A rapid centering and leveling utility that allows component alignment without any manual intervention, increasing throughput and accuracy. The end product is mathematically optimized to produce a more efficient engine, therefore reducing fuel consumption, engine noise, and increasing time on the wing.
TALYStack benefits include full integration with the measurement process, no manual input, and direct communication with the AEROStack System, delivering…
- Right first-time engine build
- Reduced engine noise
- Reduced vibration
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Reduced seal and bearing wear
Credits: Taylor Hobson
Click on the following link Metrologically Speaking to read more such blogs about the Metrology Industry.