Home
Sponsored Video
Sponsored Video
MS Blog



FAQ’S
1. What is a computed tomography scan?
Nearly every region of the body may be seen using a CT scan, which is also used to plan medical, surgical, or radiation treatments as well as detect diseases and injuries.
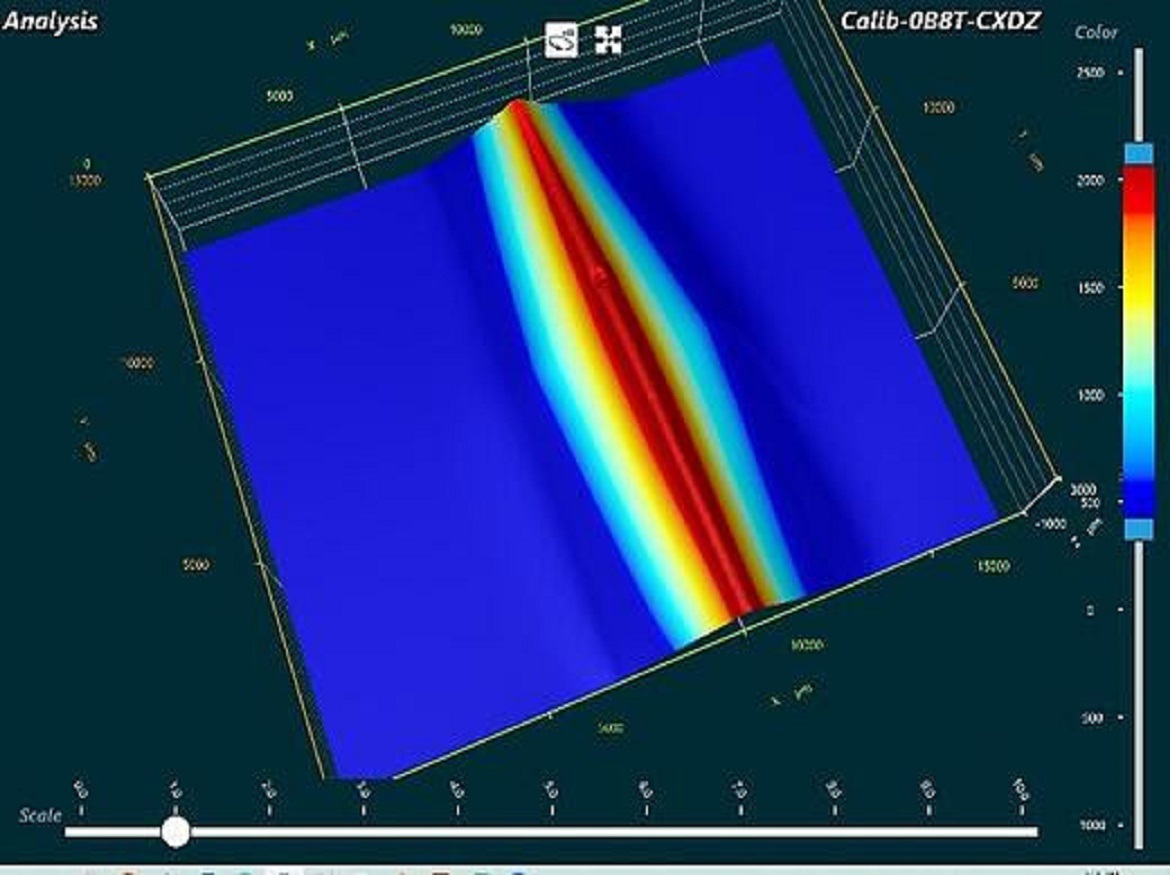
2.What is a 3D colormap comparison?
The procedure of overlaying two or more 3D data sets and showing the difference in normal deviation between them is known as a 3D colour map comparison. A user-defined colour scheme is used to symbolise that distance. A colormap’s overall appearance has been compared to that of a colour topographical map because it employs the same methods for determining colour variance.
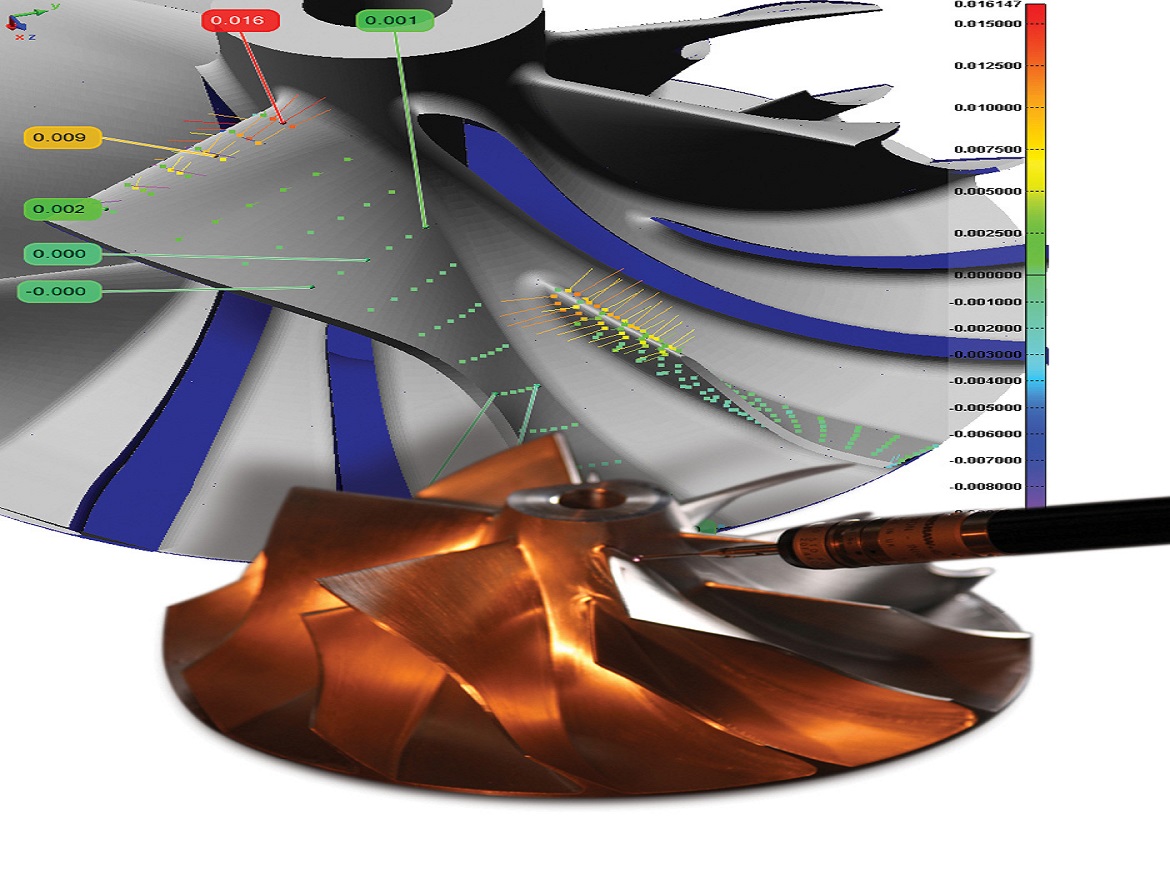
3. What is 3D metrology?
The scientific study of physical measuring is known as 3D metrology. However, it is frequently referred to in broader terms as the overall field of precise measurement in industry. Applying 3D metrology is fundamentally the very precise acquisition of an object’s geometrical data in three axes (x, y, z). Any kind of precise 3D capture device can be used to take these measurements, while coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are frequently used for this purpose.
4. What is Bluelight scanning?
The use of 3D structured light-based scanners in metrology applications is referred to as “blue light scanning.” Structured light-based scanners often produce data with the highest accuracy and resolution available in the market. The colour of the LED bulb in the system’s projector is referred to as “blue.” Systems can be ordered in a variety of hues, with blue, green, and white serving as some examples.
5. What is design intent?
A designer can establish the relationships between the aspects of a CAD model using dimensions and constraints. The term “design intent” describes how a CAD model will respond to a modification in the future.
6. What is DesignX?
An industry-leading 3D scan-to-CAD model application is Geomagic DesignX. A highly accurate, feature-based model can be reverse engineered using 3D scan data and then loaded into a number of popular CAD programmes, such as SolidWorks, Siemens NX, PTC Creo, and Autodesk Inventor.
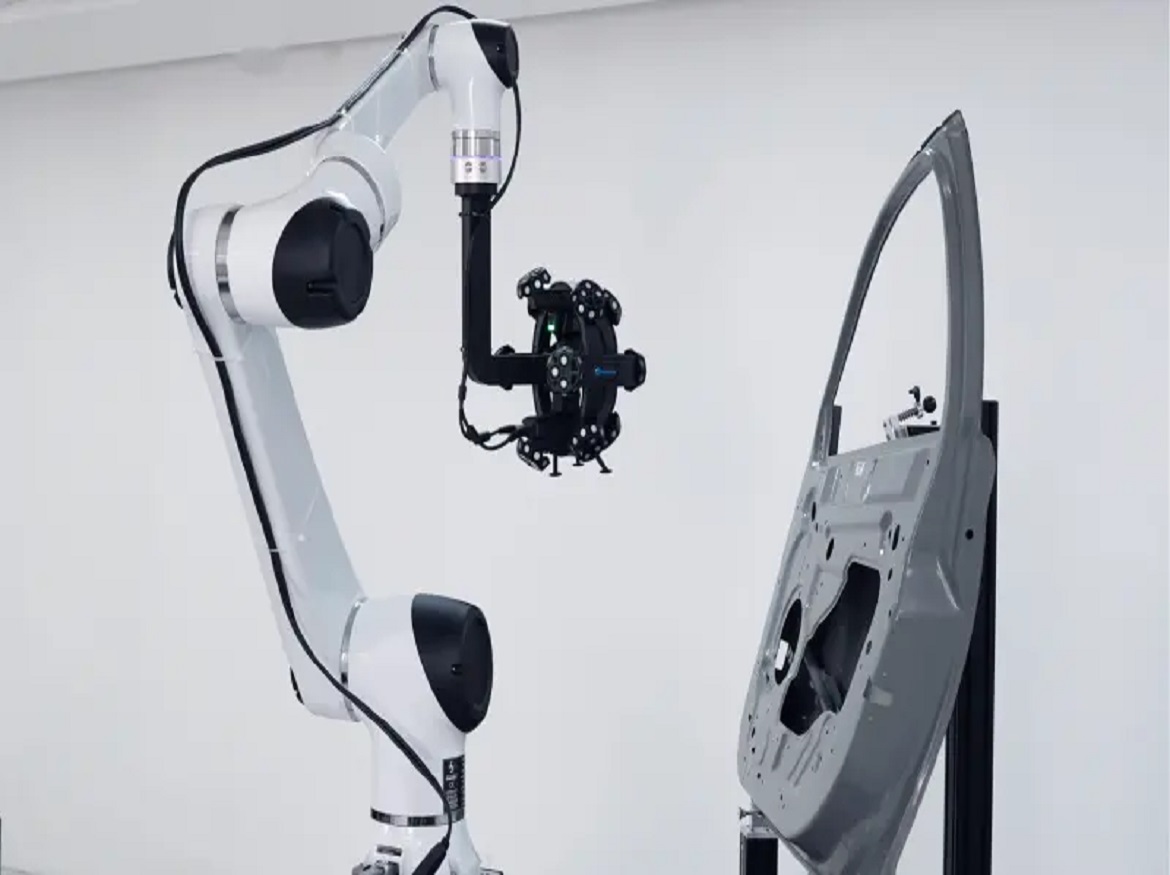
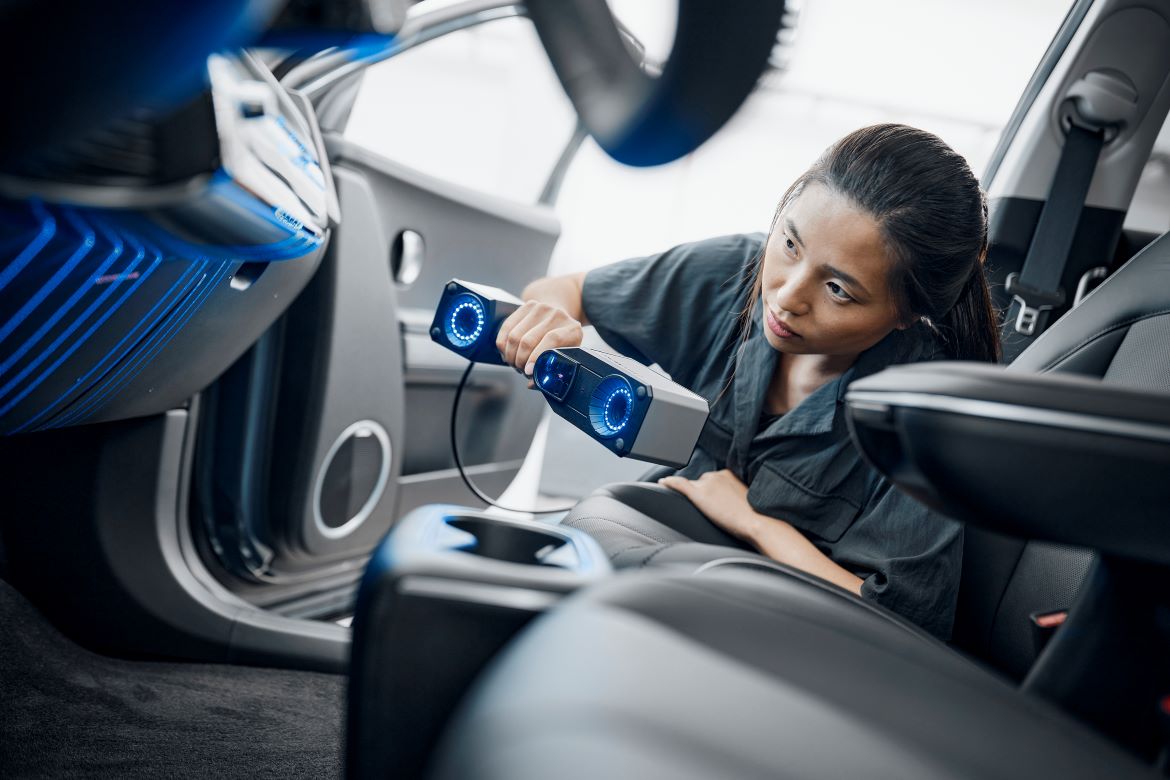
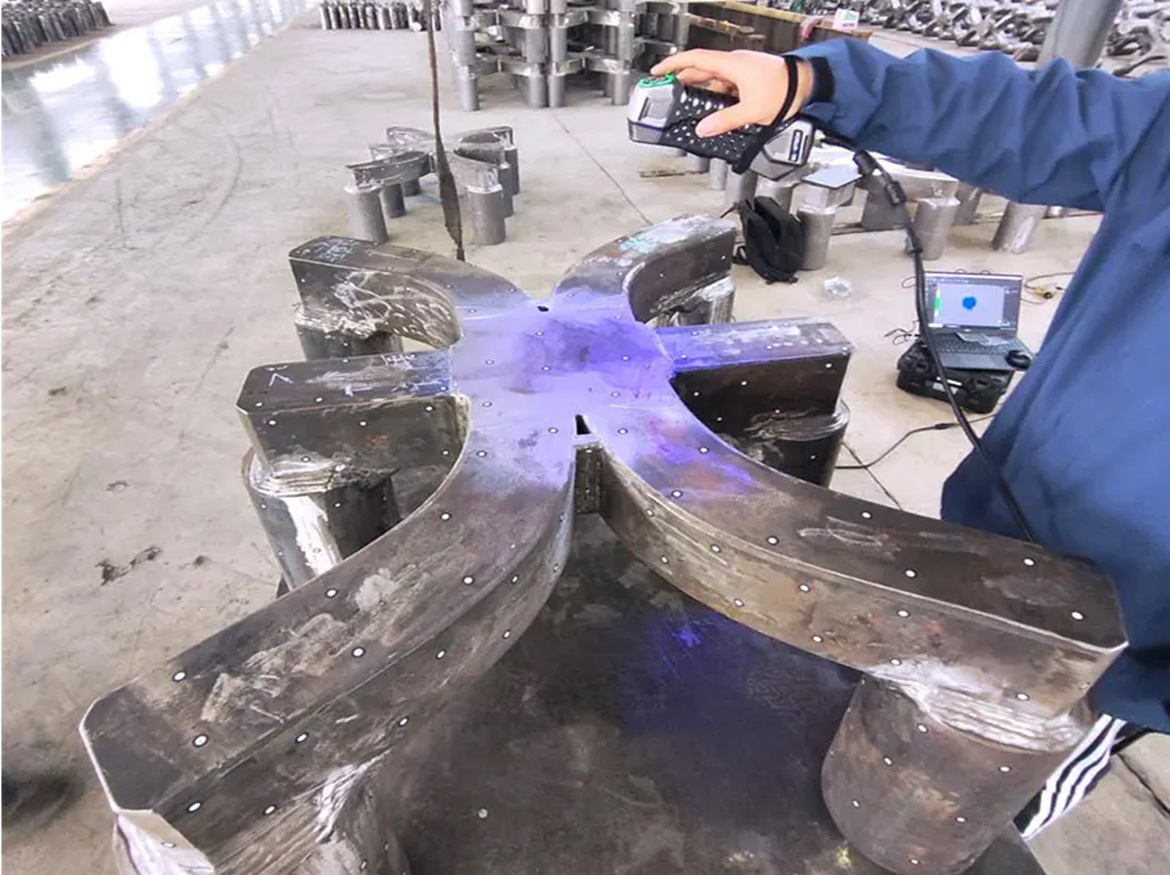
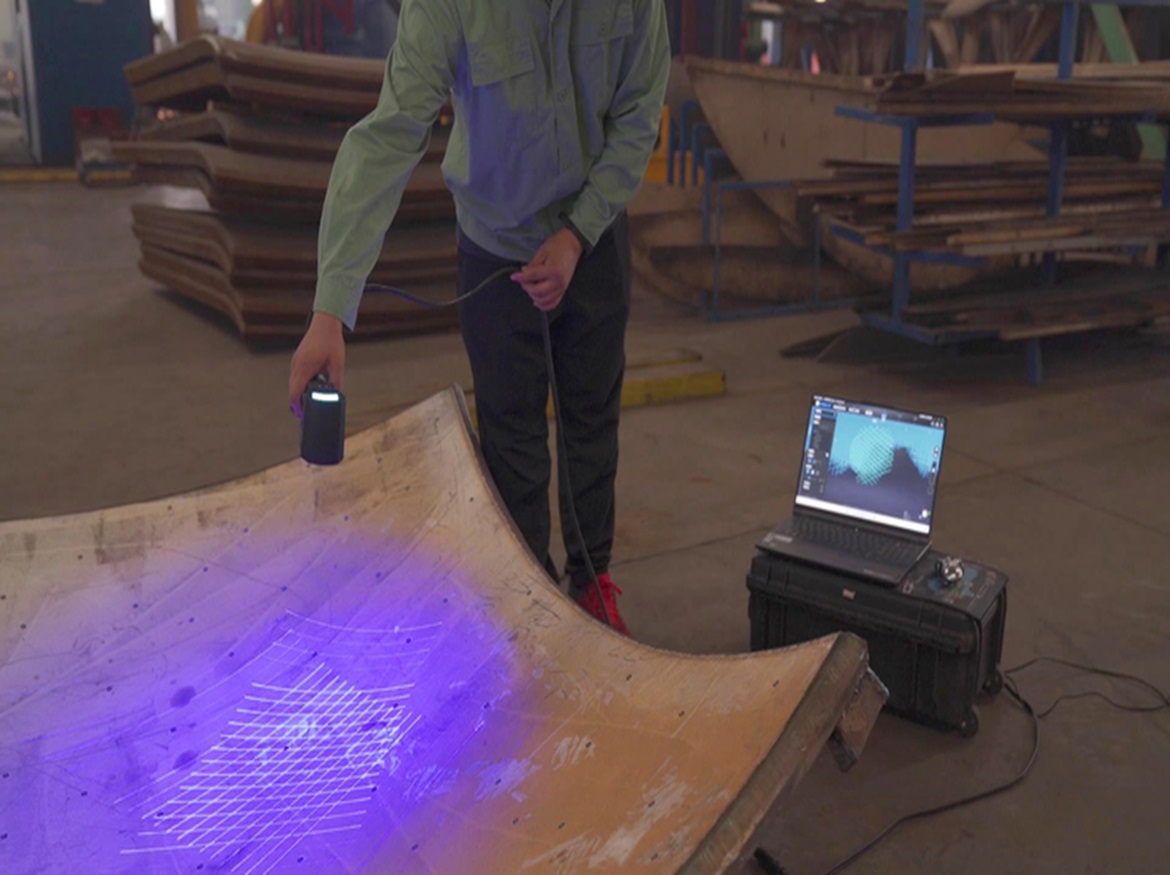
7. What is hand-held 3D scanning?
Using a hand-held 3D scanner, it is possible to capture precise 3D geometry and, in certain situations, colour data from a variety of items that are both mechanical and organic in their design. Similar to taking a series of images of an object from various angles, the procedure often involves utilising a structured light or laser scanner to gather surface data without making physical contact with the object, capturing the 3D geometry of the object instead of simply a 2D image. A number of applications, including inspection, re-engineering, and 3D printing, can utilise the obtained data.
8. What is ITAR?
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations are referred to as ITAR. The United States Munitions List is a list of rules that governs the import and export of items and services connected to defence (USML). The Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) and the State Department are in charge of and in charge of administering these restrictions. The USML is a list of goods, services, and technologies that the American government has deemed to be relevant to defence and space. In essence, the USML covers anything that has to do with the military (weapons and ammunition, armour, tanks, naval vessels), or the aerospace (fighter jets, auxiliary helicopters, spaceships). Being ITAR compliant signifies that the person or people have registered with the US Government to alert them that they are handling sensitive information.
- What is DesignX?
An industry-leading 3D scan-to-CAD model application is Geomagic DesignX. A highly accurate, feature-based model can be reverse engineered using 3D scan data and then loaded into a number of popular CAD programmes, such as SolidWorks, Siemens NX, PTC Creo, and Autodesk Inventor.
7. What is hand-held 3D scanning?
Using a hand-held 3D scanner, it is possible to capture precise 3D geometry and, in certain situations, colour data from a variety of items that are both mechanical and organic in their design. Similar to taking a series of images of an object from various angles, the procedure often involves utilising a structured light or laser scanner to gather surface data without making physical contact with the object, capturing the 3D geometry of the object instead of simply a 2D image. A number of applications, including inspection, re-engineering, and 3D printing, can utilise the obtained data.
8. What is ITAR?
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations are referred to as ITAR. The United States Munitions List is a list of rules that governs the import and export of items and services connected to defence (USML). The Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) and the State Department are in charge of and in charge of administering these restrictions. The USML is a list of goods, services, and technologies that the American government has deemed to be relevant to defence and space. In essence, the USML covers anything that has to do with the military (weapons and ammunition, armour, tanks, naval vessels), or the aerospace (fighter jets, auxiliary helicopters, spaceships). Being ITAR compliant signifies that the person or people have registered with the US Government to alert them that they are handling sensitive information.
9. What is industrial CT scanning?
In this context, computed tomography is referred to as CT. X-rays are used in CT scanning to create a significant number of 2-D images of an object’s interior and exterior. These 2-D photos are combined to generate a three-dimensional representation of the full thing. After being scanned, the part can undergo structural analysis, void analysis, fibre analysis, and other analyses in addition to the usual metrology services (inspection, reverse engineering, etc.). The majority of the time, industrial CT scanning is comparable to receiving an MRI in a hospital, but it utilises substantially more radiation and power.
10. What is laser scanning inspection?
the process of evaluating a part’s freeform surfaces and dimensional geometric features. Without regard to fundamental dimensional specifications, the user can analyse every area of the part point by point using the data from laser scanning. The ability of laser scanning inspection to spot potential discrepancies in parts that would have otherwise gone unnoticed gives it an edge over conventional techniques.
11. What is a laser tracker?
A portable coordinate measuring machine (PCMM) called a laser tracker enables incredibly accurate measurements over very long distances. Lasers, encoders, and retroreflector targets are used in the base unit of a laser tracker to precisely measure points in a 3D (X, Y, Z) coordinate system.
12. What is long-range scanning?
Any type of scanning that covers an area between about 10 metres and several square kilometres is generally referred to as long-range scanning. Buildings and huge spaces are typically scanned using this technique, and images and point cloud data are collected. BIM modelling and as-is 3D CAD models of structures are frequently produced using long-range scanning. A terrestrial LIDAR scanner is the type of scanner that is most frequently utilized in this area.
13. What is a NURBS model?
NURBS, which stands for “Non-uniform rational basis spline,” is an abbreviation. An incredibly exact model of the part in its as-is state is produced by a NURBS model, which is composed of patches fitted to scan data.
14. What is a parametric model?
A CAD-based model with a feature-based history tree is referred to as a parametric model. The history enables the end user to edit their component in their preferred CAD programme, such as Solidworks, Creo, or Autodesk.