With the continuous advancement of manufacturing technologies, the demands for precision and quality control have become increasingly stringent.
Traditional measurement methods often fall short when facing the challenges of modern manufacturing, while 3D metrology has gradually emerged as a key technology to fill this gap.
By utilizing advanced equipment such as 3D laser scanners, alongside tactile coordinate measuring machines (CMM), 3D metrology can achieve precise and accurate capture of the geometric shapes of physical components. This technology provides robust support for quality control.
In this era of relentless pursuit of excellence, 3D metrology technology not only redefines the possibilities of measurement but also offers manufacturers enduring solutions to address complex measurement requirements.

What is 3D Metrology?
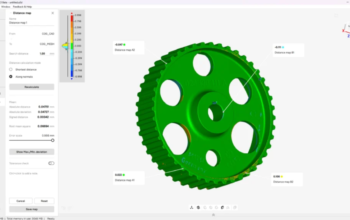
3D metrology is a specialized field focused on the precise measurement of geometric shapes, allowing for the accurate capture of three-dimensional data across the x, y, and z axes.
This technology empowers manufacturers to generate digital twin 3D models of physical objects, which are crucial for in-depth analysis, quality control, and ensuring compliance with design
specifications. By utilizing 3D metrology, companies can significantly improve their quality control measures.
Traditionally, metrologists relied on coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to collect dimensional data of manufactured parts. CMMs use contact probes to move along the x, y, and z axes to obtain multiple data points.
However, with advancements in technology, 3D metrology has begun to integrate various scanning and imaging techniques. These modern tools leverage triangulation principles, combining projected stripe patterns onto objects to accurately measure part dimensions and generate high-precision 3D models.
Why Use 3D Metrology?
• Meeting Strict Tolerance Requirements:As technology advances, parts must maintain increasingly stringent tolerances, which traditional measurement tools often cannot achieve.
• Higher Data Coverage:3D metrology can generate millions of data points in a short time, providing comprehensive surface dimension information about parts, far surpassing the few hundred data points typically collected by CMMs.
• Real-Time Process Inspection:3D metrology technology facilitates real-time measurements during production, enhancing the efficiency of quality control.
• Adaptability to Complex Products:It effectively measures complex parts with varying densities and surface finishes, ensuring higher measurement accuracy.

Types of Metrology 3D Systems
Metrology-grade 3D scanners are specialized measurement devices that meet stringent industry requirements for precision, repeatability, reliability, and ease of use.
They can capture millions of data points within seconds, generating high-resolution digital models. These scanners can also integrate with other measurement tools, such as probes or lasers, to provide additional functionality and information. Some of the most common types include:
Handheld & Portable 3D Scanners
Handheld 3D scanners offer significant mobility, making them ideal for quickly scanning medium to large objects. They are typically more affordable and user-friendly, making them particularly suitable for automated part inspection applications in industrial manufacturing.
These devices significantly enhance capture speed and measurement accuracy, enabling users to swiftly obtain the necessary data.
Their portability allows them to adapt flexibly to various object sizes and shapes, from small components to large equipment. Their adaptability ensures outstanding performance in diverse environments and conditions.

Distinctions Between Tactile and Multi-Sensor CMM
Tactile Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) perform precise measurements by physically contacting predefined points on an object’s surface with a probe.
These devices excel in providing high accuracy, making them suitable for geometrically simple objects or those requiring strict tolerances.
However, they operate at a relatively slower pace, which can limit their application in high-volume production environments.
In contrast, Multi-Sensor CMM systems offer enhanced versatility by incorporating various measurement sensors, including optical, laser, and tactile options.
This capability allows for flexible switching between different sensors to accommodate complex scanning scenarios. Multi-Sensor CMMs can efficiently measure a wider range of geometrically intricate components, providing a more comprehensive approach to quality control and inspection.
Laser and Probe Hybrid Systems
Laser and probe hybrid systems combine the benefits of laser scanning and tactile probing, effectively scanning both the surfaces and internal features of objects, such as holes or grooves.
These systems are particularly well-suited for objects with complex geometries, providing comprehensive measurement information that helps users capture detailed internal structures and external profiles.
This multifunctional equipment enhances the thoroughness and accuracy of scanning, making it applicable in various industrial and engineering settings.

Desktop 3D Scanners
Desktop 3D scanners are compact systems designed specifically for high-precision digitization of small, complex objects, commonly used in reverse engineering and quality inspection.
These devices emphasize high resolution and fine detail capture, meeting the measurement demands for small sizes and intricate surface structures.
Their efficiency and accuracy make them ideal for laboratory and office environments, providing excellent performance in relatively constrained spaces and suitable for various fine craftsmanship inspections and digitalization tasks.
Industries Utilizing 3D Metrology Technology
3D metrology is widely applied across various industries that require high-quality and high-performance products or processes. Key sectors include:
• Manufacturing
• Aerospace
• Automotive Industry
• Medical Devices
• Construction and Engineering
• Electronics and Electrical Industry
• Mold Manufacturing
• Art and Cultural Heritage Preservation
• Consumer Goods
Best metrology 3D scanners 2024
SIMSCAN-E
The SIMSCAN is a compact, lightweight 3D laser scanner perfect for small to normal-sized parts, especially in tight spaces. With its wireless design, it captures up to 6.3 million measurements per second and delivers high accuracy of 0.020 mm.
Its versatile scanning modes make it ideal for automotive components, mechanical parts, and energy tools, excelling in scanning narrow, hard-to-reach areas.

NimbleTrack
NimbleTrack is a portable, wireless 3D scanner that offers precise, target-free scanning. Compact and easy to transport, it achieves up to 0.025 mm accuracy and supports multi-tracker measurement, making it suitable for small to large parts.
Its versatility and mobility make it a top choice for industries like automotive, aviation, and cultural heritage.

TrackScan Sharp-S
TrackScan Sharp-S is designed for large-scale scanning, capable of tracking up to 8.5 meters and covering a 135 m³ measurement volume.
Fully wireless and high-speed, it delivers up to 4.86 million measurements per second with a volumetric accuracy of 0.048 (10.4 m³) mm. This makes it ideal for scanning automotive bodies, industrial equipment, and large objects where precision and speed are crucial.

Final Words
In summary, the application of 3D metrology technology is extensive, particularly excelling in enhancing product quality. This technology allows manufacturers to gain a deeper understanding of the performance of final components and their underlying factors.
With its advantages in speed, scale, and flexibility, 3D scanning has emerged as a highly attractive alternative to traditional measurement methods.