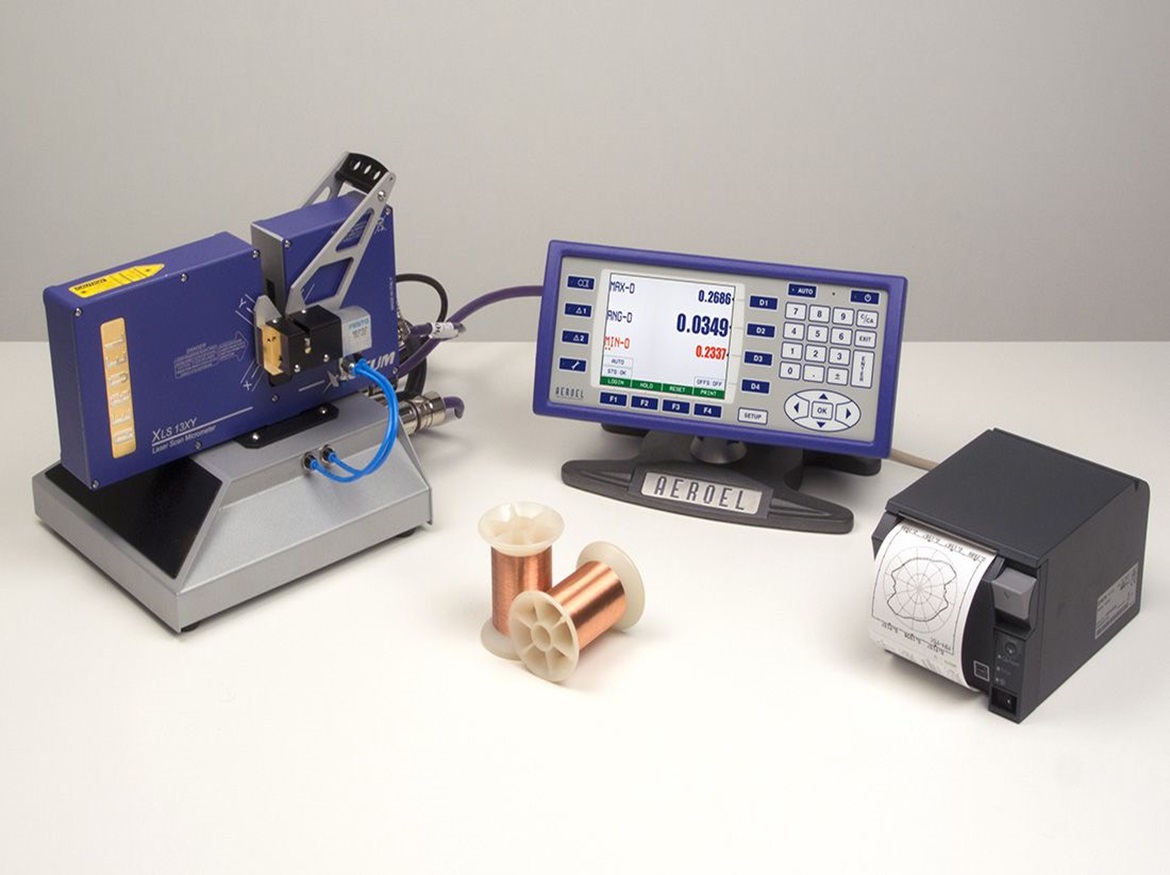
Marposs, a global leader in quality control and precision measurement solutions, marks a new milestone with the integration of a laser micrometer from Aeroel, a Group company specialising in high-precision laser measurement instrumentation, into an automated fibre optic production line on the International Space Station (ISS).
The laser micrometer was launched into orbit on the latest NASA Cygnus NG-20 resupply mission using the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. The project aims to test its glass drawing processes in microgravity conditions to produce ZBLAN optical fibers free of defects induced by terrestrial gravity. Marposs contributed to this project with its laser micrometer, normally used in the industrial measurement of wires and cables.
The device was optimized during production and then tested in the laboratory to withstand the significant vibrations and accelerations during the launch phase of the Falcon 9 rocket. By continuously measuring the diameter of the optical fiber during production, the sensor guarantees 100% dimensional quality in the production of optical fibers in space.
Marposs’ participation in this innovative project confirms its leadership in the field of laser light instruments for non-contact dimensional measurement. Laser gauges are used in numerous manufacturing processes in the mechanical industry, in the production of wire, cable and optical fibers, in plastic extrusion and many other industrial sectors. The sensor model used on the ISS can measure objects starting from 30 micrometers (30 thousandths of a millimeter) with a measurement repeatability (accuracy) of 30 nanometers, allowing the production of optical fibers with unprecedented quality in space.