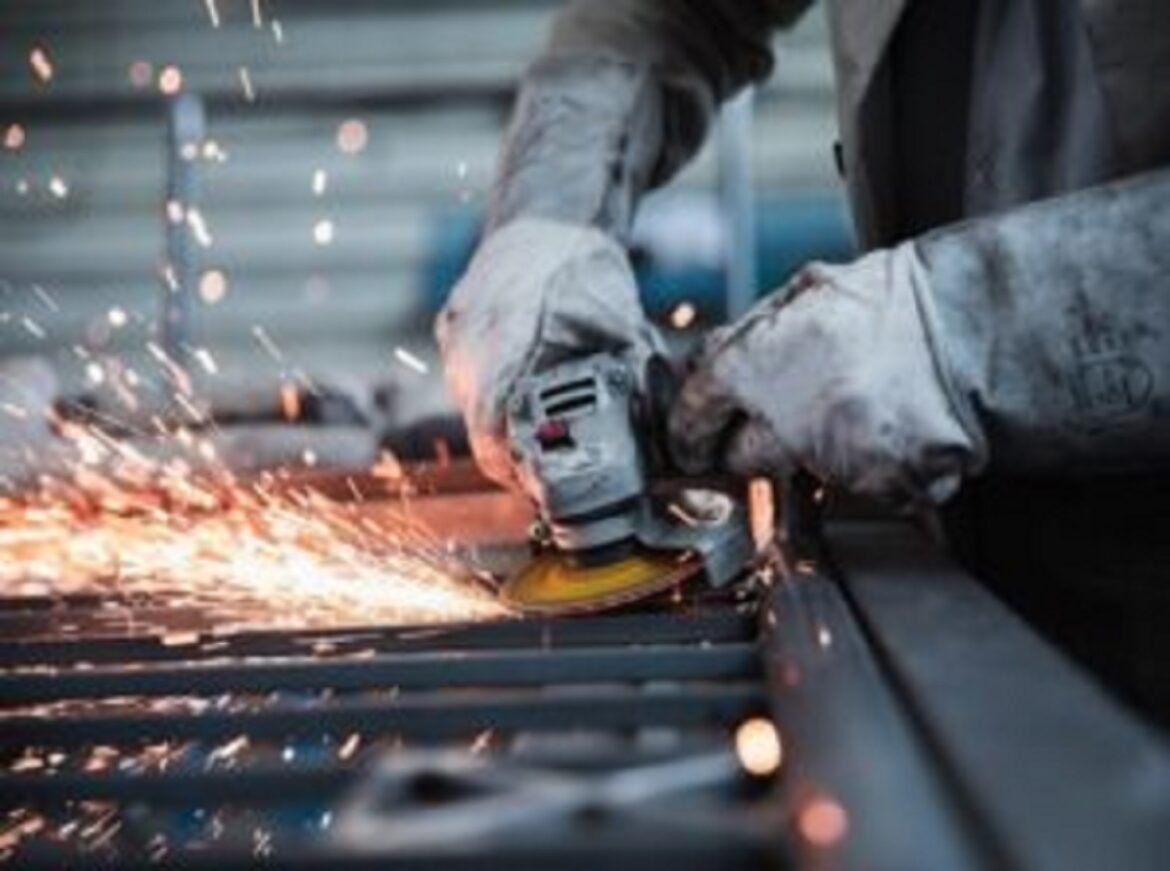
Given the fierce competition in the industry and the UK’s ranking as the ninth-largest manufacturing nation in the world, businesses are doing everything they can to reduce costs. The focus of lean manufacturing, sometimes referred to as lean production, six sigma, or kaizen, is on streamlining the manufacturing process. This specifically entails increased productivity, quicker processes, more uniformity, and more precise production.
Despite being novel, the idea has been around for more than a century, famously included in Henry Ford’s American vehicle assembly line and afterward employed extensively in Japanese manufacturing.
While lean manufacturing procedures have a number of advantages, it’s essential for manufacturers to comprehend the seven key concepts in order to fully comprehend and use them.
Waste reduction is essential for lowering the manufacturing process’s negative environmental effects and enabling economic savings. The use of 3D simulation software makes it easy to see where this can be accomplished. Manufacturers can determine where equipment can be eliminated from the real device without affecting its performance by simulating, for instance, a proposed component machining system.
2) Placing a high value on people
Lean manufacturing prioritises workers just as much as it does equipment. Leaders must make sure that staff members aren’t overworked, held responsible for accomplishments and shortcomings, and given full visibility into the outcomes of their jobs. Even the most advanced technology is useless if staff isn’t treated well and valued. Manufacturers can once more use 3D
Continuously seeking to enhance the production process entails a constant pursuit of excellence and places improvement at the core of the organizational culture. The foundation of lean manufacturing is continuous improvement and avoiding complacency at all costs. Using 3D simulation software, organizations may continuously iterate on innovations before putting them into practice.
4) Mapping the value stream
The value stream describes how a product is made in the facility, or, to put it another way, it is a map that shows the path taken by raw materials to become finished goods. Manufacturers are likely to find areas where improvements can be made by setting out this map with arrows that illustrate each process. Software for can make it possible to visualise this stream.
5) Minimizing and avoiding errors
Errors lead to material, time, and financial waste, which directly contradicts the concept of lean production. While it’s true that certain errors cannot be prevented, efficiency can be increased by minimising errors to the greatest extent possible. This can be accomplished, for example, by integrating robotics into the manufacturing line. By utilising a robot simulation to fine-tune the procedure, potential errors can be identified before they occur in the real world.
6) Detecting loss of Value
Lead times, price points, colour, the characteristics of the material(s) used, the functional and geometric requirements of the product, and the repeatability, accuracy, and precision of the parts are the aspects that make up value in the manufacturing process. Using simulation software
7) Automatically detecting flaws
When errors cannot be avoided, procedures should be in place to achieve automatic detection. This can entail locating and removing any problematic materials. For instance, if the product is being ruined by ferrous metal contamination, installing powerful magnets along the line will instantly discover flaws. The same effect might also be achieved by installing intelligent sensors or cameras.
8) Reorienting the manufacturing sector
Following these seven guidelines will give producers new options as well as improved levels of efficiency and optimization throughout the manufacturing process. Just-in-time manufacturing is one of them. Manufacturers are better equipped to produce items based simply on demand when they have a culture centred around lean processes, which helps to lower the amount of capital and money needed for manufacturing. Customers will have lengthier lead times as a result of production starting only after an order is placed, but the possibility of product waste can be eliminated.
In the end, lean manufacturing uses cutting-edge technology like automation and simulation to support a highly productive, environmentally friendly, and competitive manufacturing process. Manufacturers are better able to design a factory with this.
Read More About Us @ https://metrologicallyspeaking.com/