Optical metrology is a measurement method that collects information about an object’s physical characteristics using light. This can involve taking measurements of length, area, size, surface roughness, and other attributes. Optical metrology has several uses in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, engineering, biology, and medicine.
Optical metrology measures the characteristics of the light that interacts with the object being measured and is reflected, refracted, transmitted, or absorbed by it. This can involve measuring characteristics like distance, shape, or surface roughness using interferometry, speckle pattern analysis, or laser-structured light patterns.
Using two or more light beams to produce an interference pattern that may be used to calculate the separation between an item and a measuring instrument is known as interferometry. A rough surface’s ability to scatter light is measured using a technique called speckle pattern analysis. To build 3D maps of an object’s shape by deflecting the pattern or laser line, structured light patterns or laser lines are projected onto the part.
Applications of optical metrology
- Manufacturing and Engineering: In manufacturing and engineering, optical metrology is used to guarantee the precision and quality of parts and components. Monitoring the calibre of coatings and other surface treatments is one way to do this, as is assessing the dimensions and surface roughness of machined items.
- Biomedical and Life Sciences: The physical characteristics of cells, tissues, and organs are measured and examined using optical metrology in the biomedical and life sciences. This may entail gauging biological material surfaces for roughness and cell size and shape.
- Archaeology and Conservation: In archaeology and conservation, optical metrology is used to precisely measure and record cultural heritage items. This can involve modelling items in 3D and keeping track of deterioration in historic structures and monuments.
- Aerospace and Defense: The form and surface quality of parts and components are measured in the aerospace and defence industries using optical metrology. This can involve assessing the surface roughness of radar-absorbing materials as well as the curvature of mirrors and lenses.
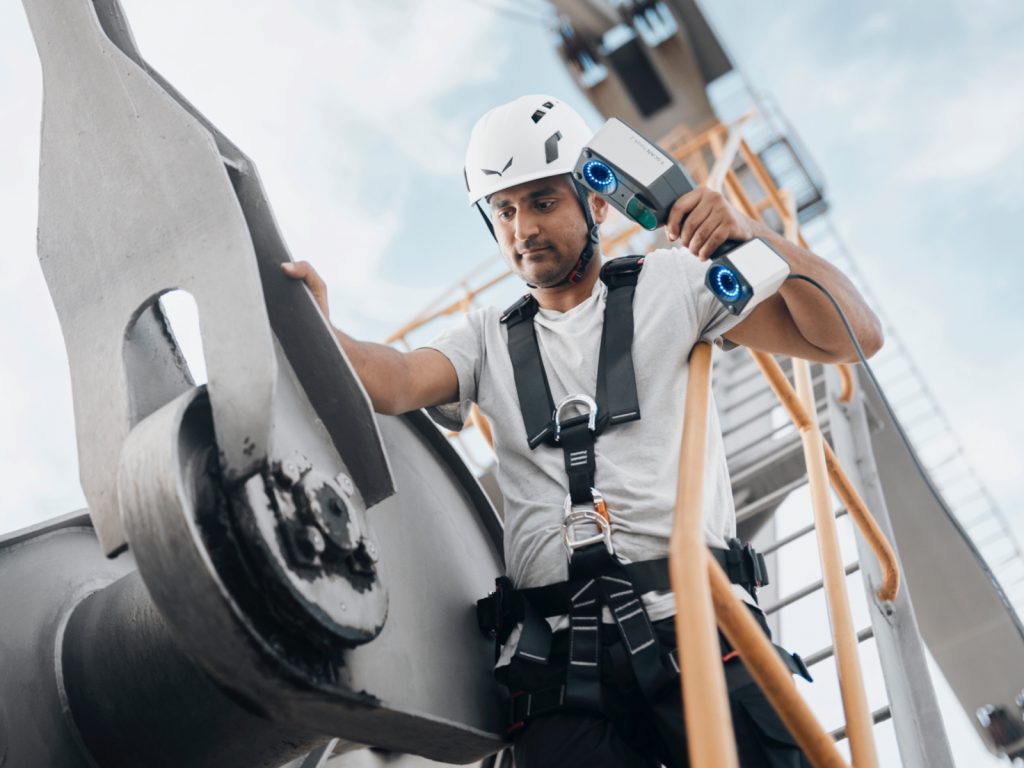

Advantages and disadvantages of optical metrology
A non-contact measurement method, optical metrology involves no direct physical touch between the thing being measured and the measuring apparatus. This can reduce the possibility of the object or part being damaged. Moreover, optical measuring techniques can produce measurements that are quite accurate, making them a useful tool for applications that need for precise measurements. Furthermore, the usage of this technology is supported by its speed. For applications that call for quick measurements, optical metrology is a useful tool since it can deliver measurements quickly.
The optical method of measurement does have some drawbacks, though, just like any other technology.
Environmental variations including temperature, humidity, and vibration can affect optical metrology. In some circumstances, this can make it more challenging to obtain precise and repeatable measurements. However, depending on the precise technique employed, optical metrology may only have a small range. Large objects or surfaces may become more challenging to measure as a result. Also, the cost of optical measurement techniques and the associated hardware may make them unaffordable for specific applications or businesses.
The perfect fit for you
By identifying the best tool for your inspection work, ZEISS optical metrology solutions assist you reduce the drawbacks. There is undoubtedly a solution for you, whether it be for use in the production area, the inspection of various parts, or part sizes.
Generally, optical metrology is a strong measurement method that collects information about an object’s physical characteristics using light. It is a useful instrument in a variety of industries and professions, from manufacturing and engineering to biomedicine and the life sciences, because to its broad range of applications and excellent accuracy. Although optical metrology has significant drawbacks, we reduce these drawbacks and optimise the benefits with our method to make it a useful tool for a variety of applications.
Click on the following link Metrologically Speaking to read more such blogs on Metrology.