Navigating your way through all the safety information available online can seem daunting, so in this blog post we introduce some of the best safety and compliance resources that can help guide you on your journey.
UR pioneered the development of robot power and force limiting technology, knowing that in bringing down the barriers to automation deployment –both literally and figuratively speaking—safety would be both an enabler of widespread cobot adoption and a necessity for successful human-robot collaboration.
And so, from the risk assessment sections of the UR User Manual to the safety guidance provided through the UR Academy to the numerous safety information resources available through UR Support, safety has always been a central consideration for UR’s approach to collaborative robot design through robot application implementation.
UR’s patented adjustable safety system allows users to adjust a range of parameters in order to reduce the risks involved with implementing industrial robot applications. These applications range from machine tending, assembly, finishing, polishing, inspection, packing, palletizing to welding.
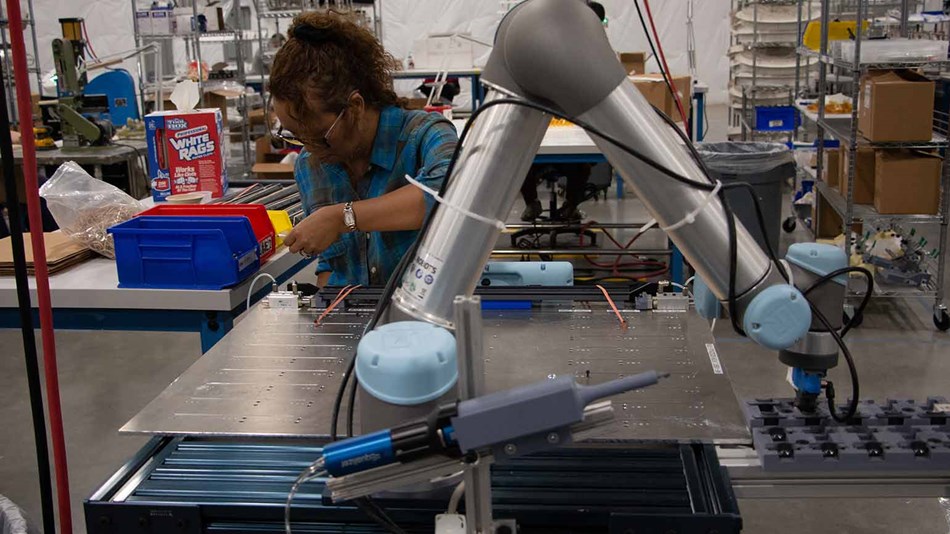

Seattle, Washington-based aerospace manufacturer Tool Gauge deployed a UR5 in a plastics assembly and dispensing application that involves close human-robot collaboration. The cobot’s force limiting safety system ensures that it will automatically stop operating if it encounters an obstacle.
These parameters include limiting the force, speed, power or momentum of the robot, and restricting its workspace using axis limits and safety boundaries. For example, the speed of Universal Robots’ cobots can be reduced while the worker is working beside it. The reduced speed enables a person to avoid contact and in the event of contact, the impact force and energy transfer is also reduced.
UR’s commitment to safety means achieving compliance with relevant safety standards for manufacturers. As a manufacturer, we do our utmost to inform our distributors and end-customers about our robots. As a result, UR leads the industry in disclosure of safety certifications and safety function details.
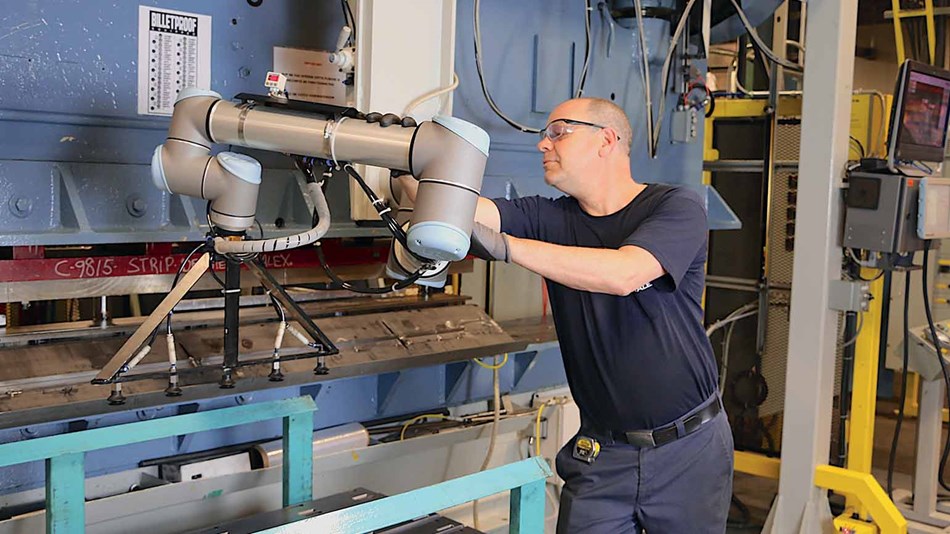

At Etalex in Montreal, Canada, a UR10 cobot tending a press brake slows down to 20% of production speed when the operator enters the workspace. The entry is detected by the SICK safety scanner that is connected with the UR robot.
Further, UR+ –an ecosystem of certified UR-compatible hardware and peripherals– provides additional safety solutions such as SICK’s easy-to-use sBot Stop package, a safety laser scanner which monitors the ground level around a cobot and can detect whenever a person enters or leaves the area. sBot Stop is easily programmed using the UR Teach Pendant.
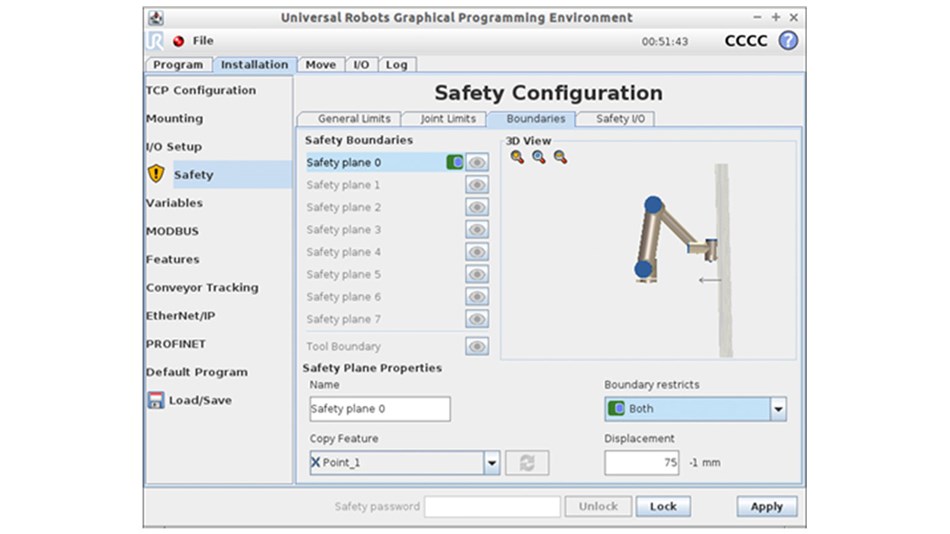
The Support section of the UR Website hosts numerous articles designed to guide users through the steps involved in various safety-related tasks. The above screenshot is part of a guide to creating a ‘Safe Home’ routine, which enables your cobot to start automatically without using the “Automove” feature.
Universal Robots Support provides a wide selection of safety articles, including a Safety FAQ and detailed guides to using our cobots’ safety features, such as ‘Setting Up Safety Boundaries’.
Here are some other great places on the UR website to learn about cobot safety:
- ‘Safety Made Easy’ –a comprehensive summary of cobot safety topics.
- ‘e-Series Safety Functions’ -explains your UR e-Series cobot’s safety functions, what they involve and what is controlled when the function is activated.
- ‘Safety FAQ’ -links to essential resources and a glossary of cobot safety terms.
UR partners, academic research groups, independent testing specialists, and industry bodies have also developed useful resources for learning about cobot safety. Let’s take a look at some of the best:
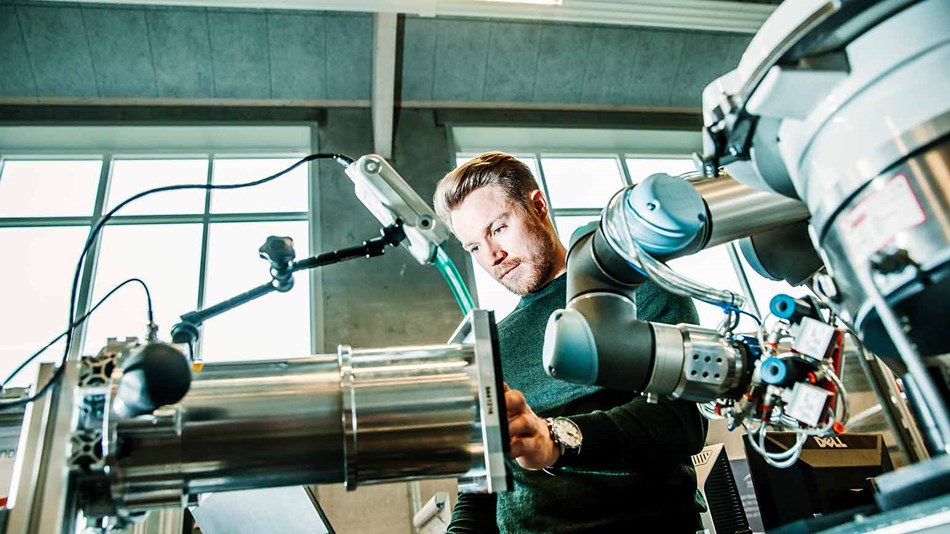

Aske Bach Lassen, project coordinator of COVR at the Danish Technological Institute (DTI), working with a Universal Robots cobot. Credit: DTI
The COVR ProjectThe European Union-funded COVR project -a collaboration between researchers from the Danish Technological Institute, National Research Council of Italy, Fraunhofer IFF, Roessingh Research & Development and CEA- recently released an ambitious, free digital toolbox that provides a central repository of information and guidance regarding risk assessments, safety directives and standards, and the safety best practices that apply to collaborative application deployments.
For beginners, COVR’s digital toolkit provides guidance on safe robot programming and how to perform a risk assessment. Meanwhile, more expert cobot users will find information on validation protocols, case stories from users in manufacturing, logistics and healthcare and up-to-date cobot safety-related publications.
TÜV Rheinland
Another welcome recent addition to the world’s collective cobot safety knowledge base comes from TÜV Rheinland, a global leader in independent inspection and certification services. Entitled ‘Robot Safety: An In-depth Exploration of Categories and Standards,’ the new ebook provides an overview of the standards governing the manufacture, integration and use of cobots, by region.
A3 Robotics
A3 Robotics (formerly known as the Robotics Industry Association) published its RIA TR15.606-2016 collaborative Robots standard in 2016. TR 606 explains safety requirements specific to collaborative robots and robot systems and is supplemental to the guidance in ANSI/RIA R15.06. (TR 606 is a U.S. National Adoption of ISO/TS 15066). The A3 website is host to a broad range of resources regarding cobot safety including Cobot Safety Training and Robot Safety Standards Documents. The robot safety documents include technical reports about risk assessment (RIA TR R15.306), existing applications (RIA TR R15.506), user requirements (RIA TR R15.706) and how to measure pressures and forces of a collaborative application (RIA TR R15.806).
It’s never too early to think about safety. So, whether you’re curious about industrial robotics, collaborative applications – as an end-user or an experienced integrator, these resources can help guide you through the principles and practice of cobot safety and compliance.
Ready to talk cobot safety with one of our experts?
AUTHOR :-
ROBERTA NELSON SHEA
Roberta Nelson Shea is the Global Technical Compliance Officer at Universal Robots responsible for product safety and reducing barriers to global acceptance and deployment. She has spent more than 40 years as a manufacturing automation professional, 23 of them additionally chairing the American National Robot Safety Committee. As chair of ANSI/RIA R15.06 she has developed and defined various technical standards for industrial robots. As chair of the committee ISO/TC 299 (ISO/TC 184/SC2), she led the introduction of ISO/TS 15066, which, as an extension of the established ISO 10218, is the first document to define standardized safety requirements for human-robot collaboration.